本文介绍下六种地理坐标系,大地坐标中央经线,以及WGS84、GCJ02、BD09、CGCS2000、UTM五种地理坐标系两两互相转化的Python和Java实现代码,包括十进制和度分秒的互转。并用Next.js开发了一个地图坐标系批量转换免费在线工具,单次最大支持10万条经纬度数据的转化。
一、WGS84
WGS84(World Geodetic System 1984)是全球定位系统(GPS)所使用的地理坐标系统和地球参考框架。它是由美国国防部开发的,广泛应用于导航、制图和地理信息系统(GIS)中。以下是一些关于WGS84坐标系统的重要资料:
1. 基本概念
- 椭球参数:
- 长半轴(a):6378137.0米
- 扁率倒数(1/f):298.257223563
- 短半轴(b):6356752.3142米
- 原点:
- 原点位于地球质心(地球的重心),在赤道和本初子午线的交点处。
- 坐标系统:
- 经度(Longitude):从本初子午线向东或向西测量,范围为-180°到+180°。
- 纬度(Latitude):从赤道向北或向南测量,范围为-90°到+90°。
- 高程(Elevation or Height):相对于椭球面的高度。
2. 应用领域
- 导航:用于航空、航海、陆地导航及GPS设备。
- 制图:地形图、海图、城市地图等都基于WGS84。
- GIS(地理信息系统):空间数据分析和管理。
- 遥感:卫星影像定位和地理数据处理。
3. 转换和比较
WGS84是全球通用的地理坐标系统,但不同的国家和地区可能使用其他的坐标系统,如中国的CGCS2000(中国大地坐标系2000)和日本的JGD2000(日本地理数据2000)。在地理信息处理和应用中,经常需要在不同坐标系统之间进行转换。常见的转换工具包括:
- Proj.4:一个用于转换地理坐标的开源库。
- GDAL(Geospatial Data Abstraction Library):用于处理和转换地理数据格式的开源库。
- Google Earth:支持多种地理坐标系统的可视化工具。
4. 精度
WGS84不断进行更新以提高其精度。最新的版本是WGS84 (G2139),其精度在几厘米至几米之间,这取决于具体的应用环境和使用的设备。
5. 参考资料
- NGA(National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency)发布的WGS84文档。
- GPS.gov:提供关于GPS及其应用的详细信息。
- OGC(Open Geospatial Consortium)标准:定义了地理信息系统的数据交换和处理规范。
如果你需要更多关于WGS84的具体技术资料或应用实例,可以访问这些组织的官方网站或相关的技术文档。
二、GCJ02
GCJ-02(火星坐标系)是中国国家测绘局制定的一种地理坐标系统,用于在中国大陆范围内的地理数据。以下是一些关于GCJ-02坐标系统的重要资料和资源链接:
1. 基本概念
- 椭球参数:
- GCJ-02的椭球参数与WGS84相同,都是基于地球的椭球模型。
- 偏移算法:
- GCJ-02坐标系基于WGS84坐标系进行了一定的加密和偏移处理,以保护国家地理信息安全。
- 偏移算法是保密的,具体实现未公开,但在开发中有各种实现方法来进行转换。
2. 应用领域
- 地图服务:高德地图、腾讯地图等中国大陆的地图服务商使用GCJ-02坐标系统。
- 导航:应用于中国大陆的各种导航设备和服务。
- 地理信息系统(GIS):在中国大陆的空间数据处理和管理。
3. 转换工具和库
- GCoord:一个JavaScript库,用于各种坐标系(包括GCJ-02和WGS84)之间的转换。
- proj4js:一个JavaScript库,用于坐标转换,支持GCJ-02。
- Python Geocoding Libraries:如
pyproj库,可用于坐标系转换和地理计算。
4. 相关标准和规范
- 国家测绘地理信息局:提供关于GCJ-02的规范和政策。
5. 应用和可视化工具
6. 参考资料
- GCJ-02和WGS84坐标转换算法:虽然官方算法保密,但网络上有一些第三方提供的转换算法和实现示例。(见文章末尾的示例)
这些链接和资源将提供你关于GCJ-02坐标系统的详细技术资料、使用指南以及相关工具和标准。如果你有特定的需求或应用场景,可以通过这些资源找到更多详细信息和支持。
三、BD09
BD-09(百度坐标系)是百度公司推出的一种地理坐标系统,它基于GCJ-02(火星坐标系)进行进一步的加密和偏移处理。BD-09坐标系广泛应用于百度地图、百度导航等百度提供的地理信息服务中。
1. 基本概念
- BD-09 坐标系:
- BD-09 坐标系是在 GCJ-02 坐标系基础上进行进一步偏移处理得到的。
- 该坐标系通过加密算法对原始坐标进行偏移,以保护地理信息数据的安全。
- 偏移算法:
- BD-09 的具体加密算法未公开,但有公开的第三方实现和逆向工程结果。
2. 应用领域
- 地图服务:百度地图等基于百度坐标系进行展示和导航。
- 导航服务:百度导航在中国大陆范围内使用 BD-09 坐标系进行定位和导航。
- 地理信息系统(GIS):百度提供的地理数据和服务采用 BD-09 坐标系。
3. 转换工具和库
- Python 坐标转换库:如
pyproj库,可用于坐标系转换和地理计算。 - 坐标转换算法示例:提供 WGS84、GCJ-02 和 BD-09 坐标系之间的转换算法。(见文章尾部示例)
- GCoord:一个 JavaScript 库,用于各种坐标系(包括 BD-09、GCJ-02 和 WGS84)之间的转换。
4. 相关标准和规范
- 国家测绘地理信息局:提供关于地理坐标系的规范和政策。
5. 应用和可视化工具
6. 参考资料
- 百度地图 API 文档:提供关于 BD-09 坐标系使用和转换的详细说明。
- GCJ-02 和 BD-09 坐标转换算法:虽然官方算法保密,但网络上有一些第三方提供的转换算法和实现示例。(见文章末尾的示例)
这些链接和资源将提供你关于 BD-09 坐标系统的详细技术资料、使用指南以及相关工具和标准。如果你有特定的需求或应用场景,可以通过这些资源找到更多详细信息和支持。
四、CGCS2000
CGCS2000(China Geodetic Coordinate System 2000)是中国大地坐标系2000,是中国国家测绘地理信息局(NGCC)建立的地理坐标系,广泛应用于国家测绘、地理信息系统(GIS)和导航等领域。
1. 基本概念
- 参考椭球参数:
- 长半轴(a):6378137.0米
- 扁率倒数(1/f):298.257222101
- 地心引力常数 GM=3.986004418×1014m3s-2
- 自转角速度 ω=7.292l15×10-5rad s-1
- 原点:
- 原点位于地球质心,参照国际大地参考框架(ITRF)。
- 坐标系统:
- 经度(Longitude):从本初子午线向东或向西测量,范围为-180°到+180°。
- 纬度(Latitude):从赤道向北或向南测量,范围为-90°到+90°。
- 高程(Elevation or Height):相对于椭球面的高度。
2. 应用领域
- 测绘:国家大地测量、工程测量和基础地理信息数据采集。
- 导航:北斗导航系统和其他导航设备。
- GIS:空间数据分析、城市规划和资源管理等。
3. 转换工具和库
- Proj.4:一个用于坐标转换的开源库,支持CGCS2000和其他常见坐标系。
- GDAL(Geospatial Data Abstraction Library):用于处理和转换地理数据格式的开源库。
- 中国国家测绘地理信息局:提供CGCS2000的标准和技术规范。
4. 相关标准和规范
- CGCS2000 坐标系技术规定:详细定义了CGCS2000的技术细节和应用规范。
- ITRF(International Terrestrial Reference Frame):CGCS2000是基于ITRF的坐标系。
5. 应用和可视化工具
6. 参考资料
- CGCS2000 介绍:详细介绍CGCS2000坐标系的文章和文档。
- 测绘科学研究院:提供关于CGCS2000的研究和应用信息。
这些链接和资源将提供你关于CGCS2000坐标系统的详细技术资料、使用指南以及相关工具和标准。如果你有特定的需求或应用场景,可以通过这些资源找到更多详细信息和支持。
五、UTM
1. 什么是UTM坐标系?
UTM(Universal Transverse Mercator)坐标系是基于横轴墨卡托投影的一种地理坐标系,将地球表面划分为多个投影带,每个投影带覆盖6度经度范围。UTM坐标系以米为单位,用来表示地理位置。
2. UTM坐标系的特点
- 分区:
- 地球表面被划分为60个纵向带区,每个带区宽6度经度。
- 带区编号从西经180度开始,从1到60。
- 每个带区又进一步划分为北半球和南半球。
- 坐标表示:
- 东向偏移(Easting):从带区中央经线开始,向东以米为单位计量。中央经线的东向偏移通常设为500,000米,以避免负值。
- 北向偏移(Northing):从赤道开始,向北以米为单位计量。在北半球从赤道开始计量;在南半球,赤道的北向偏移设为10,000,000米,以避免负值。
3. UTM坐标格式
一个典型的UTM坐标由以下部分组成:
- 东向偏移(Easting):以米为单位,从带区中央经线开始。
- 北向偏移(Northing):以米为单位,从赤道开始。
- 带区编号(Zone Number):表示经度范围,从1到60。
- 带区字母(Zone Letter):表示纬度范围,从C到X(不包括I和O),每个字母带区的纬度范围为8度。
4. 示例:
例如,以下是一个UTM坐标的示例:
- 东向偏移:500,000米
- 北向偏移:4,649,776米
- 带区编号:33
- 带区字母:T
5. UTM和WGS84格式之间的转换
常规处理默认是使用6度分带,在某些情况下,为了提高精度,可以使用3度分带的UTM坐标系,即每个带区宽3度经度,而不是通常的6度。这种情况下,带区编号的范围会变成1到120。
六、BJ54
BJ54(北京1954坐标系)是中国在1954年建立的大地坐标系统,它基于克拉索夫斯基椭球(Krasovsky ellipsoid)并广泛应用于中国的测绘和地理信息系统中,特别是在CGCS2000(中国大地坐标系2000)建立之前。以下是有关BJ54坐标系的详细信息及相关链接资源。
基本概念
- 椭球参数:
- 长半轴(a):6378245.0米
- 扁率倒数(1/f):298.3
- 投影方式:
- BJ54常使用高斯-克吕格(Gauss-Krüger)投影,将地理坐标转换为平面坐标。
- 在高斯-克吕格投影中,中国通常使用6度分带。
- 参考大地原点:
- 原点设在北京观象台(北纬39°54′40.90″,东经116°27′43.95″)。
应用领域
- 测绘:20世纪中期至21世纪初,中国的大部分测绘工作都是基于BJ54坐标系进行的。
- 工程测量:在CGCS2000坐标系普及之前,BJ54坐标系被广泛用于工程测量和国土资源管理。
- 地理信息系统(GIS):早期的GIS数据通常使用BJ54坐标系存储和分析。
转换工具和库
- Proj.4:一个用于坐标转换的开源库,支持BJ54坐标系与其他坐标系的转换。
- GDAL(Geospatial Data Abstraction Library):支持多种坐标系转换,包括BJ54。
- 中国国家测绘地理信息局:提供中国坐标系的标准和技术规范。
相关标准和规范
- 国家标准:关于BJ54坐标系的使用和技术规范。
- 地理坐标系转换标准:描述了BJ54和其他坐标系之间的转换方法和公式。
应用和可视化工具
参考资料
- 中国测绘科学研究院:提供关于BJ54的研究和应用信息。
这些链接和资源将提供你关于BJ54坐标系统的详细技术资料、使用指南以及相关工具和标准。如果你有特定的需求或应用场景,可以通过这些资源找到更多详细信息和支持。
七、大地坐标中央经线
在大地坐标转换中,6度分带和3度分带的参数主要用于高斯-克吕格(Gauss-Krüger)投影和UTM(Universal Transverse Mercator)投影。这些投影方法将球面坐标转换为平面坐标,适用于大比例尺地图制图和精确的地理信息系统(GIS)分析。在WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09和CGCS2000坐标系之间的转换中,6度分带和3度分带的参数并不直接使用,因为这些转换主要是地理坐标系之间的转换,而不是投影坐标系之间的转换。
1. 中央经线参考表信息
中央经线参考表在高斯-克吕格投影和UTM投影中起关键作用。这些参考表提供了不同分带系统下各带的中央经线值:
- 6度分带:
- 每个带宽6度,中央经线从3度起始,以6度递增。
- 例如,第一个带的中央经线是3度,第二个带是9度,依此类推。
- 3度分带:
- 每个带宽3度,中央经线从1.5度起始,以3度递增。
- 例如,第一个带的中央经线是1.5度,第二个带是4.5度,依此类推。
2. 在坐标系转换中的使用
在直接进行WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09和CGCS2000地理坐标系之间的转换时,不涉及平面坐标系(如高斯-克吕格或UTM)的转换,因此不需要使用6度分带和3度分带的参数。这些转换主要涉及椭球参数和偏移算法。
然而,如果你需要将地理坐标转换为平面坐标,或者将平面坐标转换为地理坐标,则需要使用6度分带和3度分带的参数。常规的处理默认使用标准的6度分带,如果需要使用3度分带,需要自定义转换逻辑,例如:
- 从地理坐标(WGS84)到UTM坐标:
- 需要确定地理坐标所在的UTM带,并使用该带的中央经线进行投影转换。
- 从UTM坐标到地理坐标(WGS84):
- 需要使用相应的中央经线和带宽参数将平面坐标转换回地理坐标。
3. 举例说明
例如,在使用高斯-克吕格投影时,转换步骤可能包括:
- 地理坐标到高斯-克吕格平面坐标:
- 确定分带(6度或3度),找到对应的中央经线。
- 使用高斯-克吕格投影公式将地理坐标转换为平面坐标。
- 高斯-克吕格平面坐标到地理坐标:
- 使用相应的中央经线和分带信息,应用逆高斯-克吕格公式将平面坐标转换回地理坐标。
总之,6度分带和3度分带的参数在高斯-克吕格和UTM投影中至关重要,但在纯地理坐标系(如WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09、CGCS2000)之间的转换中不需要使用这些参数。如果你的应用涉及到从地理坐标到投影坐标的转换(或反之),则需要考虑这些分带参数。
4. 6度分带
| 带号 | 经度范围 | 中央经线 |
| 1 | -180° to -174° | -177 |
| 2 | -174° to -168° | -171 |
| 3 | -168° to -162° | -165 |
| 4 | -162° to -156° | -159 |
| 5 | -156° to -150° | -153 |
| 6 | -150° to -144° | -147 |
| 7 | -144° to -138° | -141 |
| 8 | -138° to -132° | -135 |
| 9 | -132° to -126° | -129 |
| 10 | -126° to -120° | -123 |
| 11 | -120° to -114° | -117 |
| 12 | -114° to -108° | -111 |
| 13 | -108° to -102° | -105 |
| 14 | -102° to -96° | -99 |
| 15 | -96° to -90° | -93 |
| 16 | -90° to -84° | -87 |
| 17 | -84° to -78° | -81 |
| 18 | -78° to -72° | -75 |
| 19 | -72° to -66° | -69 |
| 20 | -66° to -60° | -63 |
| 21 | -60° to -54° | -57 |
| 22 | -54° to -48° | -51 |
| 23 | -48° to -42° | -45 |
| 24 | -42° to -36° | -39 |
| 25 | -36° to -30° | -33 |
| 26 | -30° to -24° | -27 |
| 27 | -24° to -18° | -21 |
| 28 | -18° to -12° | -15 |
| 29 | -12° to -6° | -9 |
| 30 | -6° to 0° | -3 |
| 31 | 0° to 6° | 3 |
| 32 | 6° to 12° | 9 |
| 33 | 12° to 18° | 15 |
| 34 | 18° to 24° | 21 |
| 35 | 24° to 30° | 27 |
| 36 | 30° to 36° | 33 |
| 37 | 36° to 42° | 39 |
| 38 | 42° to 48° | 45 |
| 39 | 48° to 54° | 51 |
| 40 | 54° to 60° | 57 |
| 41 | 60° to 66° | 63 |
| 42 | 66° to 72° | 69 |
| 43 | 72° to 78° | 75 |
| 44 | 78° to 84° | 81 |
| 45 | 84° to 90° | 87 |
| 46 | 90° to 96° | 93 |
| 47 | 96° to 102° | 99 |
| 48 | 102° to 108° | 105 |
| 49 | 108° to 114° | 111 |
| 50 | 114° to 120° | 117 |
| 51 | 120° to 126° | 123 |
| 52 | 126° to 132° | 129 |
| 53 | 132° to 138° | 135 |
| 54 | 138° to 144° | 141 |
| 55 | 144° to 150° | 147 |
| 56 | 150° to 156° | 153 |
| 57 | 156° to 162° | 159 |
| 58 | 162° to 168° | 165 |
| 59 | 168° to 174° | 171 |
| 60 | 174° to 180° | 177 |
5. 3度分带
| 带号 (Zone Number) | 经度范围 (Longitude Range) | 中央经线 (Central Meridian) |
| 1 | -1.5°E ~ 1.5°E | 0°E |
| 2 | 1.5°E ~ 4.5°E | 3°E |
| 3 | 4.5°E ~ 7.5°E | 6°E |
| 4 | 7.5°E ~ 10.5°E | 9°E |
| 5 | 10.5°E ~ 13.5°E | 12°E |
| 6 | 13.5°E ~ 16.5°E | 15°E |
| 7 | 16.5°E ~ 19.5°E | 18°E |
| 8 | 19.5°E ~ 22.5°E | 21°E |
| 9 | 22.5°E ~ 25.5°E | 24°E |
| 10 | 25.5°E ~ 28.5°E | 27°E |
| 11 | 28.5°E ~ 31.5°E | 30°E |
| 12 | 31.5°E ~ 34.5°E | 33°E |
| 13 | 34.5°E ~ 37.5°E | 36°E |
| 14 | 37.5°E ~ 40.5°E | 39°E |
| 15 | 40.5°E ~ 43.5°E | 42°E |
| 16 | 43.5°E ~ 46.5°E | 45°E |
| 17 | 46.5°E ~ 49.5°E | 48°E |
| 18 | 49.5°E ~ 52.5°E | 51°E |
| 19 | 52.5°E ~ 55.5°E | 54°E |
| 20 | 55.5°E ~ 58.5°E | 57°E |
| 21 | 58.5°E ~ 61.5°E | 60°E |
| 22 | 61.5°E ~ 64.5°E | 63°E |
| 23 | 64.5°E ~ 67.5°E | 66°E |
| 24 | 67.5°E ~ 70.5°E | 69°E |
| 25 | 70.5°E ~ 73.5°E | 72°E |
| 26 | 73.5°E ~ 76.5°E | 75°E |
| 27 | 76.5°E ~ 79.5°E | 78°E |
| 28 | 79.5°E ~ 82.5°E | 81°E |
| 29 | 82.5°E ~ 85.5°E | 84°E |
| 30 | 85.5°E ~ 88.5°E | 87°E |
| 31 | 88.5°E ~ 91.5°E | 90°E |
| 32 | 91.5°E ~ 94.5°E | 93°E |
| 33 | 94.5°E ~ 97.5°E | 96°E |
| 34 | 97.5°E ~ 100.5°E | 99°E |
| 35 | 100.5°E ~ 103.5°E | 102°E |
| 36 | 103.5°E ~ 106.5°E | 105°E |
| 37 | 106.5°E ~ 109.5°E | 108°E |
| 38 | 109.5°E ~ 112.5°E | 111°E |
| 39 | 112.5°E ~ 115.5°E | 114°E |
| 40 | 115.5°E ~ 118.5°E | 117°E |
| 41 | 118.5°E ~ 121.5°E | 120°E |
| 42 | 121.5°E ~ 124.5°E | 123°E |
| 43 | 124.5°E ~ 127.5°E | 126°E |
| 44 | 127.5°E ~ 130.5°E | 129°E |
| 45 | 130.5°E ~ 133.5°E | 132°E |
| 46 | 133.5°E ~ 136.5°E | 135°E |
| 47 | 136.5°E ~ 139.5°E | 138°E |
| 48 | 139.5°E ~ 142.5°E | 141°E |
| 49 | 142.5°E ~ 145.5°E | 144°E |
| 50 | 145.5°E ~ 148.5°E | 147°E |
| 51 | 148.5°E ~ 151.5°E | 150°E |
| 52 | 151.5°E ~ 154.5°E | 153°E |
| 53 | 154.5°E ~ 157.5°E | 156°E |
| 54 | 157.5°E ~ 160.5°E | 159°E |
| 55 | 160.5°E ~ 163.5°E | 162°E |
| 56 | 163.5°E ~ 166.5°E | 165°E |
| 57 | 166.5°E ~ 169.5°E | 168°E |
| 58 | 169.5°E ~ 172.5°E | 171°E |
| 59 | 172.5°E ~ 175.5°E | 174°E |
| 60 | 175.5°E ~ 178.5°E | 177°E |
| 61 | 178.5°E ~ 181.5°E | 180°E |
| 62 | 181.5°E ~ 184.5°E | 183°E |
| 63 | 184.5°E ~ 187.5°E | 186°E |
| 64 | 187.5°E ~ 190.5°E | 189°E |
| 65 | 190.5°E ~ 193.5°E | 192°E |
| 66 | 193.5°E ~ 196.5°E | 195°E |
| 67 | 196.5°E ~ 199.5°E | 198°E |
| 68 | 199.5°E ~ 202.5°E | 201°E |
| 69 | 202.5°E ~ 205.5°E | 204°E |
| 70 | 205.5°E ~ 208.5°E | 207°E |
| 71 | 208.5°E ~ 211.5°E | 210°E |
| 72 | 211.5°E ~ 214.5°E | 213°E |
| 73 | 214.5°E ~ 217.5°E | 216°E |
| 74 | 217.5°E ~ 220.5°E | 219°E |
| 75 | 220.5°E ~ 223.5°E | 222°E |
| 76 | 223.5°E ~ 226.5°E | 225°E |
| 77 | 226.5°E ~ 229.5°E | 228°E |
| 78 | 229.5°E ~ 232.5°E | 231°E |
| 79 | 232.5°E ~ 235.5°E | 234°E |
| 80 | 235.5°E ~ 238.5°E | 237°E |
| 81 | 238.5°E ~ 241.5°E | 240°E |
| 82 | 241.5°E ~ 244.5°E | 243°E |
| 83 | 244.5°E ~ 247.5°E | 246°E |
| 84 | 247.5°E ~ 250.5°E | 249°E |
| 85 | 250.5°E ~ 253.5°E | 252°E |
| 86 | 253.5°E ~ 256.5°E | 255°E |
| 87 | 256.5°E ~ 259.5°E | 258°E |
| 88 | 259.5°E ~ 262.5°E | 261°E |
| 89 | 262.5°E ~ 265.5°E | 264°E |
| 90 | 265.5°E ~ 268.5°E | 267°E |
| 91 | 268.5°E ~ 271.5°E | 270°E |
| 92 | 271.5°E ~ 274.5°E | 273°E |
| 93 | 274.5°E ~ 277.5°E | 276°E |
| 94 | 277.5°E ~ 280.5°E | 279°E |
| 95 | 280.5°E ~ 283.5°E | 282°E |
| 96 | 283.5°E ~ 286.5°E | 285°E |
| 97 | 286.5°E ~ 289.5°E | 288°E |
| 98 | 289.5°E ~ 292.5°E | 291°E |
| 99 | 292.5°E ~ 295.5°E | 294°E |
| 100 | 295.5°E ~ 298.5°E | 297°E |
| 101 | 298.5°E ~ 301.5°E | 300°E |
| 102 | 301.5°E ~ 304.5°E | 303°E |
| 103 | 304.5°E ~ 307.5°E | 306°E |
| 104 | 307.5°E ~ 310.5°E | 309°E |
| 105 | 310.5°E ~ 313.5°E | 312°E |
| 106 | 313.5°E ~ 316.5°E | 315°E |
| 107 | 316.5°E ~ 319.5°E | 318°E |
| 108 | 319.5°E ~ 322.5°E | 321°E |
| 109 | 322.5°E ~ 325.5°E | 324°E |
| 110 | 325.5°E ~ 328.5°E | 327°E |
| 111 | 328.5°E ~ 331.5°E | 330°E |
| 112 | 331.5°E ~ 334.5°E | 333°E |
| 113 | 334.5°E ~ 337.5°E | 336°E |
| 114 | 337.5°E ~ 340.5°E | 339°E |
| 115 | 340.5°E ~ 343.5°E | 342°E |
| 116 | 343.5°E ~ 346.5°E | 345°E |
| 117 | 346.5°E ~ 349.5°E | 348°E |
| 118 | 349.5°E ~ 352.5°E | 351°E |
| 119 | 352.5°E ~ 355.5°E | 354°E |
| 120 | 355.5°E ~ 358.5°E | 357°E |
八、坐标系转化示例代码
以下是WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09、CGCS2000、UTM、DMS(度分秒)和Decimal(十进制)坐标系之间互相转换的示例代码实现,分别用Java和Python实现。
1. Java 实现
import org.geotools.referencing.CRS;
import org.geotools.referencing.crs.DefaultGeographicCRS;
import org.geotools.referencing.operation.MathTransform;
import org.opengis.referencing.FactoryException;
import org.opengis.referencing.NoSuchAuthorityCodeException;
import org.opengis.referencing.operation.TransformException;
public class CoordinateTransform {
private static final double PI = 3.1415926535897932384626;
private static final double X_PI = PI * 3000.0 / 180.0;
private static final double A = 6378245.0;
private static final double EE = 0.00669342162296594323;
// WGS84 to GCJ-02
public static double[] wgs84ToGcj02(double lat, double lon) {
if (outOfChina(lat, lon)) {
return new double[]{lat, lon};
}
double dLat = transformLat(lon - 105.0, lat - 35.0);
double dLon = transformLon(lon - 105.0, lat - 35.0);
double radLat = lat / 180.0 * PI;
double magic = Math.sin(radLat);
magic = 1 - EE * magic * magic;
double sqrtMagic = Math.sqrt(magic);
dLat = (dLat * 180.0) / ((A * (1 - EE)) / (magic * sqrtMagic) * PI);
dLon = (dLon * 180.0) / (A / sqrtMagic * Math.cos(radLat) * PI);
double mgLat = lat + dLat;
double mgLon = lon + dLon;
return new double[]{mgLat, mgLon};
}
// GCJ-02 to WGS84
public static double[] gcj02ToWgs84(double lat, double lon) {
double[] gcj02 = wgs84ToGcj02(lat, lon);
double dLat = gcj02[0] - lat;
double dLon = gcj02[1] - lon;
return new double[]{lat - dLat, lon - dLon};
}
// GCJ-02 to BD-09
public static double[] gcj02ToBd09(double lat, double lon) {
double z = Math.sqrt(lon * lon + lat * lat) + 0.00002 * Math.sin(lat * X_PI);
double theta = Math.atan2(lat, lon) + 0.000003 * Math.cos(lon * X_PI);
double bdLon = z * Math.cos(theta) + 0.0065;
double bdLat = z * Math.sin(theta) + 0.006;
return new double[]{bdLat, bdLon};
}
// BD-09 to GCJ-02
public static double[] bd09ToGcj02(double lat, double lon) {
double x = lon - 0.0065;
double y = lat - 0.006;
double z = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y) - 0.00002 * Math.sin(y * X_PI);
double theta = Math.atan2(y, x) - 0.000003 * Math.cos(x * X_PI);
double gcjLon = z * Math.cos(theta);
double gcjLat = z * Math.sin(theta);
return new double[]{gcjLat, gcjLon};
}
// WGS84 to BD-09
public static double[] wgs84ToBd09(double lat, double lon) {
double[] gcj02 = wgs84ToGcj02(lat, lon);
return gcj02ToBd09(gcj02[0], gcj02[1]);
}
// BD-09 to WGS84
public static double[] bd09ToWgs84(double lat, double lon) {
double[] gcj02 = bd09ToGcj02(lat, lon);
return gcj02ToWgs84(gcj02[0], gcj02[1]);
}
// CGCS2000 to WGS84
public static double[] cgcs2000ToWgs84(double lat, double lon) {
return new double[]{lat, lon}; // Assume CGCS2000 is equivalent to WGS84 for simplicity
}
// WGS84 to CGCS2000
public static double[] wgs84ToCgcs2000(double lat, double lon) {
return new double[]{lat, lon}; // Assume CGCS2000 is equivalent to WGS84 for simplicity
}
// GCJ-02 to CGCS2000
public static double[] gcj02ToCgcs2000(double lat, double lon) {
double[] wgs84 = gcj02ToWgs84(lat, lon);
return wgs84ToCgcs2000(wgs84[0], wgs84[1]);
}
// CGCS2000 to GCJ-02
public static double[] cgcs2000ToGcj02(double lat, double lon) {
double[] wgs84 = cgcs2000ToWgs84(lat, lon);
return wgs84ToGcj02(wgs84[0], wgs84[1]);
}
// WGS84 to UTM
public static UTMResult WGS84ToUTM(double latitude, double longitude) throws NoSuchAuthorityCodeException, FactoryException, TransformException {
int zoneNumber = (int) Math.floor((longitude + 180) / 6) + 1;
boolean isNorthernHemisphere = latitude >= 0;
String utmCRS = "EPSG:" + (isNorthernHemisphere ? "326" : "327") + zoneNumber;
MathTransform transform = CRS.findMathTransform(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84, CRS.decode(utmCRS));
double[] src = new double[]{longitude, latitude};
double[] dest = new double[2];
transform.transform(src, 0, dest, 0, 1);
char zoneLetter = getUTMLetterDesignator(latitude);
return new UTMResult(dest[0], dest[1], zoneNumber, zoneLetter);
}
// UTM to WGS84
public static double[] UTMToWGS84(double easting, double northing, int zoneNumber, char zoneLetter) throws NoSuchAuthorityCodeException, FactoryException, TransformException {
boolean isNorthernHemisphere = (zoneLetter >= 'N');
String utmCRS = "EPSG:" + (isNorthernHemisphere ? "326" : "327") + zoneNumber;
MathTransform transform = CRS.findMathTransform(CRS.decode(utmCRS), DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
double[] src = new double[]{easting, northing};
double[] dest = new double[2];
transform.transform(src, 0, dest, 0, 1);
return dest;
}
private static char getUTMLetterDesignator(double latitude) {
if ((84 >= latitude) && (latitude >= 72)) return 'X';
else if ((72 > latitude) && (latitude >= 64)) return 'W';
else if ((64 > latitude) && (latitude >= 56)) return 'V';
else if ((56 > latitude) && (latitude >= 48)) return 'U';
else if ((48 > latitude) && (latitude >= 40)) return 'T';
else if ((40 > latitude) && (latitude >= 32)) return 'S';
else if ((32 > latitude) && (latitude >= 24)) return 'R';
else if ((24 > latitude) && (latitude >= 16)) return 'Q';
else if ((16 > latitude) && (latitude >= 8)) return 'P';
else if ((8 > latitude) && (latitude >= 0)) return 'N';
else if ((0 > latitude) && (latitude >= -8)) return 'M';
else if ((-8 > latitude) && (latitude >= -16)) return 'L';
else if ((-16 > latitude) && (latitude >= -24)) return 'K';
else if ((-24 > latitude) && (latitude >= -32)) return 'J';
else if ((-32 > latitude) && (latitude >= -40)) return 'H';
else if ((-40 > latitude) && (latitude >= -48)) return 'G';
else if ((-48 > latitude) && (latitude >= -56)) return 'F';
else if ((-56 > latitude) && (latitude >= -64)) return 'E';
else if ((-64 > latitude) && (latitude >= -72)) return 'D';
else if ((-72 > latitude) && (latitude >= -80)) return 'C';
else return 'Z'; // Latitude is outside the UTM limits
}
static class UTMResult {
double easting;
double northing;
int zoneNumber;
char zoneLetter;
public UTMResult(double easting, double northing, int zoneNumber, char zoneLetter) {
this.easting = easting;
this.northing = northing;
this.zoneNumber = zoneNumber;
this.zoneLetter = zoneLetter;
}
}
// DMS to Decimal
public static double[] dmsToDecimal(String dmsLat, String dmsLon) {
double lat = convertDMSToDecimal(dmsLat);
double lon = convertDMSToDecimal(dmsLon);
return new double[]{lat, lon};
}
private static double convertDMSToDecimal(String dms) {
String[] dmsParts = dms.split("[°'\"]");
double degrees = Double.parseDouble(dmsParts[0]);
double minutes = Double.parseDouble(dmsParts[1]);
double seconds = Double.parseDouble(dmsParts[2]);
String direction = dmsParts[3];
double decimal = degrees + (minutes / 60) + (seconds / 3600);
if (direction.equals("S") || direction.equals("W")) {
decimal *= -1;
}
return decimal;
}
// Decimal to DMS
public static String[] decimalToDMS(double decimalLat, double decimalLon) {
String latDMS = convertDecimalToDMS(decimalLat, true);
String lonDMS = convertDecimalToDMS(decimalLon, false);
return new String[]{latDMS, lonDMS};
}
private static String convertDecimalToDMS(double decimal, boolean isLatitude) {
String direction;
if (isLatitude) {
direction = decimal >= 0 ? "N" : "S";
} else {
direction = decimal >= 0 ? "E" : "W";
}
decimal = Math.abs(decimal);
int degrees = (int) decimal;
double minutesNotTruncated = (decimal - degrees) * 60;
int minutes = (int) minutesNotTruncated;
double seconds = (minutesNotTruncated - minutes) * 60;
return degrees + "°" + minutes + "'" + String.format("%.2f", seconds) + "\"" + direction;
}
private static boolean outOfChina(double lat, double lon) {
return (lon < 72.004 || lon > 137.8347) || (lat < 0.8293 || lat > 55.8271);
}
private static double transformLat(double x, double y) {
double ret = -100.0 + 2.0 * x + 3.0 * y + 0.2 * y * y + 0.1 * x * y + 0.2 * Math.sqrt(Math.abs(x));
ret += (20.0 * Math.sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * Math.sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
ret += (20.0 * Math.sin(y * PI) + 40.0 * Math.sin(y / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
ret += (160.0 * Math.sin(y / 12.0 * PI) + 320.0 * Math.sin(y * PI / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
return ret;
}
private static double transformLon(double x, double y) {
double ret = 300.0 + x + 2.0 * y + 0.1 * x * x + 0.1 * x * y + 0.1 * Math.sqrt(Math.abs(x));
ret += (20.0 * Math.sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * Math.sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
ret += (20.0 * Math.sin(x * PI) + 40.0 * Math.sin(x / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
ret += (150.0 * Math.sin(x / 12.0 * PI) + 300.0 * Math.sin(x / 30.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0;
return ret;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
double lat = 39.90960456049752;
double lon = 116.3972282409668;
// WGS84 to GCJ-02
double[] gcj02 = wgs84ToGcj02(lat, lon);
System.out.println("WGS84 to GCJ-02: " + gcj02[0] + ", " + gcj02[1]);
// GCJ-02 to BD-09
double[] bd09 = gcj02ToBd09(gcj02[0], gcj02[1]);
System.out.println("GCJ-02 to BD-09: " + bd09[0] + ", " + bd09[1]);
// BD-09 to GCJ-02
double[] gcj02FromBd09 = bd09ToGcj02(bd09[0], bd09[1]);
System.out.println("BD-09 to GCJ-02: " + gcj02FromBd09[0] + ", " + gcj02FromBd09[1]);
// GCJ-02 to WGS84
double[] wgs84FromGcj02 = gcj02ToWgs84(gcj02FromBd09[0], gcj02FromBd09[1]);
System.out.println("GCJ-02 to WGS84: " + wgs84FromGcj02[0] + ", " + wgs84FromGcj02[1]);
// WGS84 to BD-09
double[] bd09FromWgs84 = wgs84ToBd09(lat, lon);
System.out.println("WGS84 to BD-09: " + bd09FromWgs84[0] + ", " + bd09FromWgs84[1]);
// BD-09 to WGS84
double[] wgs84FromBd09 = bd09ToWgs84(bd09FromWgs84[0], bd09FromWgs84[1]);
System.out.println("BD-09 to WGS84: " + wgs84FromBd09[0] + ", " + wgs84FromBd09[1]);
// CGCS2000 to WGS84
double[] wgs84FromCgcs2000 = cgcs2000ToWgs84(lat, lon);
System.out.println("CGCS2000 to WGS84: " + wgs84FromCgcs2000[0] + ", " + wgs84FromCgcs2000[1]);
// WGS84 to CGCS2000
double[] cgcs2000FromWgs84 = wgs84ToCgcs2000(lat, lon);
System.out.println("WGS84 to CGCS2000: " + cgcs2000FromWgs84[0] + ", " + cgcs2000FromWgs84[1]);
// GCJ-02 to CGCS2000
double[] cgcs2000FromGcj02 = gcj02ToCgcs2000(gcj02[0], gcj02[1]);
System.out.println("GCJ-02 to CGCS2000: " + cgcs2000FromGcj02[0] + ", " + cgcs2000FromGcj02[1]);
// CGCS2000 to GCJ-02
double[] gcj02FromCgcs2000 = cgcs2000ToGcj02(lat, lon);
System.out.println("CGCS2000 to GCJ-02: " + gcj02FromCgcs2000[0] + ", " + gcj02FromCgcs2000[1]);
// WGS84 to UTM
UTMResult utm = WGS84ToUTM(lat, lon);
System.out.println("UTM: Easting: " + utm.easting + ", Northing: " + utm.northing + ", Zone Number: " + utm.zoneNumber + ", Zone Letter: " + utm.zoneLetter);
// UTM to WGS84
double[] wgs84 = UTMToWGS84(utm.easting, utm.northing, utm.zoneNumber, utm.zoneLetter);
System.out.println("WGS84: Latitude: " + wgs84[0] + ", Longitude: " + wgs84[1]);
// DMS to Decimal
String dmsLat = "23°3'3.78\"N";
String dmsLon = "113°22'17.36\"E";
double[] decimalCoords = dmsToDecimal(dmsLat, dmsLon);
System.out.println("Decimal: Latitude: " + decimalCoords[0] + ", Longitude: " + decimalCoords[1]);
// Decimal to DMS
String[] dmsCoords = decimalToDMS(lat, lon);
System.out.println("DMS: Latitude: " + dmsCoords[0] + ", Longitude: " + dmsCoords[1]);
}
}2. Python实现
import math
import utm
X_PI = 3.14159265358979324 * 3000.0 / 180.0
PI = 3.1415926535897932384626
A = 6378245.0
EE = 0.00669342162296594323
def transformLat(x, y):
ret = -100.0 + 2.0 * x + 3.0 * y + 0.2 * y * y + 0.1 * x * y + 0.2 * math.sqrt(abs(x))
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * math.sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(y * PI) + 40.0 * math.sin(y / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (160.0 * math.sin(y / 12.0 * PI) + 320.0 * math.sin(y * PI / 30.0)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
def transformLon(x, y):
ret = 300.0 + x + 2.0 * y + 0.1 * x * x + 0.1 * x * y + 0.1 * math.sqrt(abs(x))
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(6.0 * x * PI) + 20.0 * math.sin(2.0 * x * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (20.0 * math.sin(x * PI) + 40.0 * math.sin(x / 3.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
ret += (150.0 * math.sin(x / 12.0 * PI) + 300.0 * math.sin(x / 30.0 * PI)) * 2.0 / 3.0
return ret
def wgs84_to_gcj02(lat, lon):
if out_of_china(lat, lon):
return lat, lon
dLat = transformLat(lon - 105.0, lat - 35.0)
dLon = transformLon(lon - 105.0, lat - 35.0)
radLat = lat / 180.0 * PI
magic = math.sin(radLat)
magic = 1 - EE * magic * magic
sqrtMagic = math.sqrt(magic)
dLat = (dLat * 180.0) / ((A * (1 - EE)) / (magic * sqrtMagic) * PI)
dLon = (dLon * 180.0) / (A / sqrtMagic * math.cos(radLat) * PI)
mgLat = lat + dLat
mgLon = lon + dLon
return mgLat, mgLon
def gcj02_to_wgs84(lat, lon):
gcj02 = wgs84_to_gcj02(lat, lon)
dLat = gcj02[0] - lat
dLon = gcj02[1] - lon
return lat - dLat, lon - dLon
def gcj02_to_bd09(lat, lon):
z = math.sqrt(lon * lon + lat * lat) + 0.00002 * math.sin(lat * X_PI)
theta = math.atan2(lat, lon) + 0.000003 * math.cos(lon * X_PI)
bd_lon = z * math.cos(theta) + 0.0065
bd_lat = z * math.sin(theta) + 0.006
return bd_lat, bd_lon
def bd09_to_gcj02(lat, lon):
x = lon - 0.0065
y = lat - 0.006
z = math.sqrt(x * x + y * y) - 0.00002 * math.sin(y * X_PI)
theta = math.atan2(y, x) - 0.000003 * math.cos(x * X_PI)
gcj_lon = z * math.cos(theta)
gcj_lat = z * math.sin(theta)
return gcj_lat, gcj_lon
def wgs84_to_bd09(lat, lon):
gcj02 = wgs84_to_gcj02(lat, lon)
return gcj02_to_bd09(gcj02[0], gcj02[1])
def bd09_to_wgs84(lat, lon):
gcj02 = bd09_to_gcj02(lat, lon)
return gcj02_to_wgs84(gcj02[0], gcj02[1])
def cgcs2000_to_wgs84(lat, lon):
return lat, lon # Assume CGCS2000 is equivalent to WGS84 for simplicity
def wgs84_to_cgcs2000(lat, lon):
return lat, lon # Assume CGCS2000 is equivalent to WGS84 for simplicity
def gcj02_to_cgcs2000(lat, lon):
wgs84 = gcj02_to_wgs84(lat, lon)
return wgs84_to_cgcs2000(wgs84[0], wgs84[1])
def cgcs2000_to_gcj02(lat, lon):
wgs84 = cgcs2000_to_wgs84(lat, lon)
return wgs84_to_gcj02(wgs84[0], wgs84[1])
# WGS84 to UTM
def WGS84ToUTM(latitude, longitude):
u = utm.from_latlon(latitude, longitude)
return u
# UTM to WGS84
def UTMToWGS84(easting, northing, zone_number, zone_letter):
latlon = utm.to_latlon(easting, northing, zone_number, zone_letter)
return latlon
def dms_to_decimal(dms_lat, dms_lon):
lat = convert_dms_to_decimal(dms_lat)
lon = convert_dms_to_decimal(dms_lon)
return lat, lon
def convert_dms_to_decimal(dms):
degrees, minutes, seconds, direction = re.split('[°\'"]', dms)
decimal = float(degrees) + float(minutes) / 60 + float(seconds) / 3600
if direction in ['S', 'W']:
decimal *= -1
return decimal
def decimal_to_dms(decimal_lat, decimal_lon):
lat_dms = convert_decimal_to_dms(decimal_lat, True)
lon_dms = convert_decimal_to_dms(decimal_lon, False)
return lat_dms, lon_dms
def convert_decimal_to_dms(decimal, is_latitude):
direction = 'N' if is_latitude else 'E'
if decimal < 0:
direction = 'S' if is_latitude else 'W'
decimal = abs(decimal)
degrees = int(decimal)
minutes = int((decimal - degrees) * 60)
seconds = (decimal - degrees - minutes / 60) * 3600
return f'{degrees}°{minutes}\'{seconds:.2f}"{direction}'
def out_of_china(lat, lon):
return lon < 72.004 or lon > 137.8347 or lat < 0.8293 or lat > 55.8271
if __name__ == "__main__":
lat = 39.90960456049752
lon = 116.3972282409668
# WGS84 to GCJ-02
gcj02 = wgs84_to_gcj02(lat, lon)
print("WGS84 to GCJ-02: ", gcj02)
# GCJ-02 to BD-09
bd09 = gcj02_to_bd09(gcj02[0], gcj02[1])
print("GCJ-02 to BD-09: ", bd09)
# BD-09 to GCJ-02
gcj02_from_bd09 = bd09_to_gcj02(bd09[0], bd09[1])
print("BD-09 to GCJ-02: ", gcj02_from_bd09)
# GCJ-02 to WGS84
wgs84_from_gcj02 = gcj02_to_wgs84(gcj02_from_bd09[0], gcj02_from_bd09[1])
print("GCJ-02 to WGS84: ", wgs84_from_gcj02)
# WGS84 to BD-09
bd09_from_wgs84 = wgs84_to_bd09(lat, lon)
print("WGS84 to BD-09: ", bd09_from_wgs84)
# BD-09 to WGS84
wgs84_from_bd09 = bd09_to_wgs84(bd09_from_wgs84[0], bd09_from_wgs84[1])
print("BD-09 to WGS84: ", wgs84_from_bd09)
# CGCS2000 to WGS84
wgs84_from_cgcs2000 = cgcs2000_to_wgs84(lat, lon)
print("CGCS2000 to WGS84: ", wgs84_from_cgcs2000)
# WGS84 to CGCS2000
cgcs2000_from_wgs84 = wgs84_to_cgcs2000(lat, lon)
print("WGS84 to CGCS2000: ", cgcs2000_from_wgs84)
# GCJ-02 to CGCS2000
cgcs2000_from_gcj02 = gcj02_to_cgcs2000(gcj02[0], gcj02[1])
print("GCJ-02 to CGCS2000: ", cgcs2000_from_gcj02)
# CGCS2000 to GCJ-02
gcj02_from_cgcs2000 = cgcs2000_to_gcj02(lat, lon)
print("CGCS2000 to GCJ-02: ", gcj02_from_cgcs2000)
# WGS84 to UTM
utm_coords = WGS84ToUTM(lat, lon)
print(f"UTM: Easting: {utm_coords[0]}, Northing: {utm_coords[1]}, Zone Number: {utm_coords[2]}, Zone Letter: {utm_coords[3]}")
# UTM to WGS84
wgs84_coords = UTMToWGS84(utm_coords[0], utm_coords[1], utm_coords[2], utm_coords[3])
print(f"WGS84: Latitude: {wgs84_coords[0]}, Longitude: {wgs84_coords[1]}")
# DMS to Decimal
dms_lat = "23°3'3.78\"N"
dms_lon = "113°22'17.36\"E"
decimal_coords = dms_to_decimal(dms_lat, dms_lon)
print(f"Decimal: Latitude: {decimal_coords[0]}, Longitude: {decimal_coords[1]}")
# Decimal to DMS
dms_coords = decimal_to_dms(lat, lon)
print(f"DMS: Latitude: {dms_coords[0]}, Longitude: {dms_coords[1]}")以上代码实现了WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09、CGCS2000和UTM坐标系之间的相互转换,以及Decimal(十进制经纬度)和DMS(度分秒经纬度)格式的相互转换。请注意,CGCS2000坐标系通常被认为与WGS84非常接近,因此在此示例中假设它们是等效的。根据具体的应用需求,可能需要更精确的转换方法。
九、地理坐标系批量转化在线工具
看了下目前线上的转化工具,免费的只支持单个坐标的转化,批量转化还需要注册账号充值之后才可以用,而且一次性只能支持5000条。于是做了一个WGS84、GCJ-02、BD-09、CGCS2000和UTM之间两两互相转化的在线工具,也支持DMS(度分秒)和Decimal(十进制)两种经纬度格式的互转:https://latlongconverter.online/,支持单个和批量的经纬度坐标系转化,批量转化最大支持10万行数据,支持转化之后的数据一键复制或保存为Excel文档。
网站使用Vercel服务器运行,也用Cloudflare加速了,但因为部署在美国,国内网络访问首次加载可能比较慢,有开VPN的话加载速度很快,不影响使用。
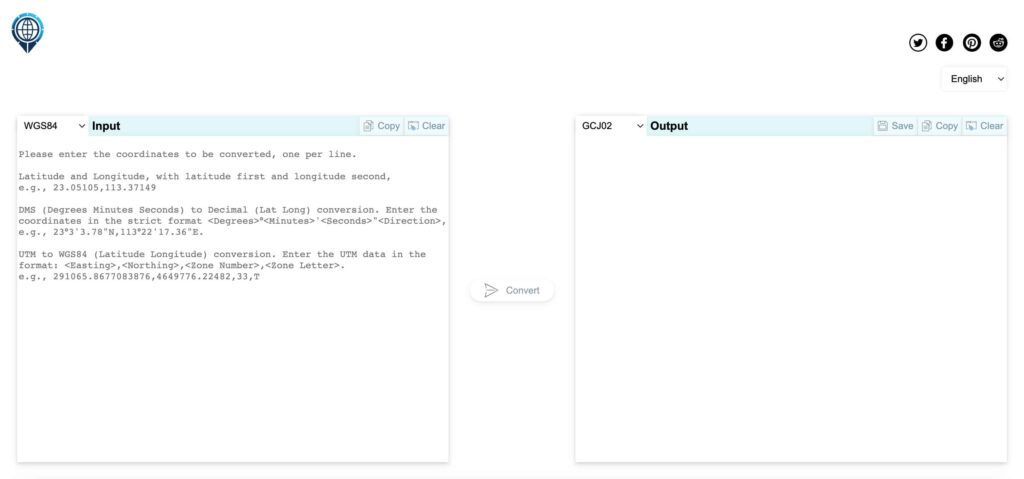
另:在2024.8.11新增了ETRS89、JGD2011、JGD2000、PRS92、ED50、HTRS96、GDM2000、Clarke 1880、BJ54、Indian 1975坐标和WGS84互转的功能,对于这些坐标的说明已在 https://latlongconverter.online/ 网站输入框下方列出,此处不再贴重复的内容说明。
新增的坐标大多需要做七参数转换,需要七参数输入的时候会在转换按钮上方显示七参数输入框面板,七参数转换需要的参数是保密的,网站只是提供一个转换功能支持,网站也不会保存用户任何的转换坐标数据和七参数数据。
BJ54和WGS84之间也需要七参数进行转换,WGS84可以等价CGCS2000坐标,如果需要BJ54转CGCS2000,可以直接使用BJ54和WGS84互转的功能。
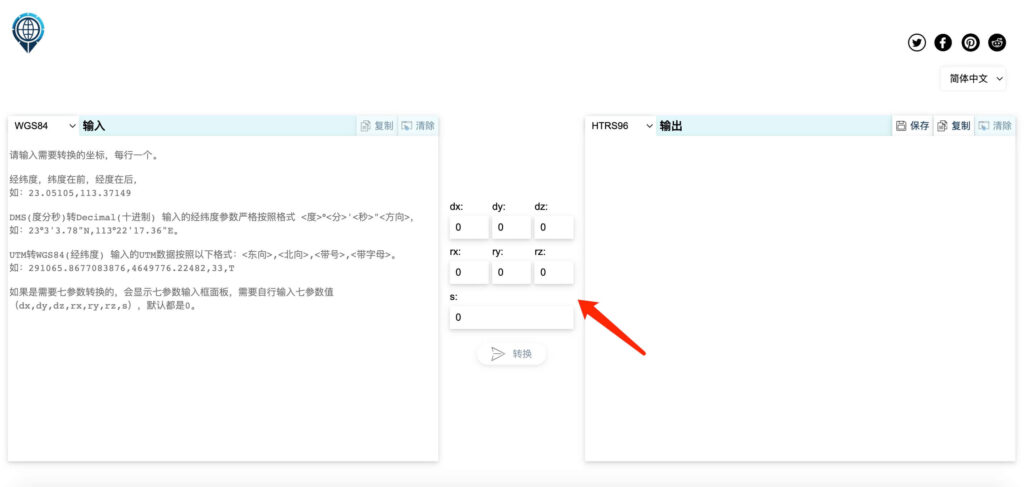
9.1 七参数定义说明
七参数转换是一种常用的地理坐标系之间的转换方法,用于将一个参考椭球上的坐标转换到另一个参考椭球。这个转换模型包括三个平移参数、三个旋转参数和一个尺度参数,总共七个参数,因此称为“七参数”。
9.1.1 平移参数(Translation Parameters)
- dx:沿X轴方向的平移,单位为米(m)。
- dy:沿Y轴方向的平移,单位为米(m)。
- dz:沿Z轴方向的平移,单位为米(m)。
9.1.2 旋转参数(Rotation Parameters)
- rx:绕X轴的旋转角度,单位为弧度(rad)。有时也以秒为单位,需要将其转换为弧度使用。
- ry:绕Y轴的旋转角度,单位为弧度(rad)。
- rz:绕Z轴的旋转角度,单位为弧度(rad)。
9.1.3 尺度参数(Scale Parameter)
- s:尺度因子,通常以百万分之一(ppm, parts per million)为单位。如果尺度因子为1ppm,那么尺度因子的值为 s = 1 * 10^-6。
扩展阅读:

微信公众号
转载请注明出处:陈文管的博客 – WGS84、GCJ02、BD09、CGCS2000、UTM和BJ54地理坐标系详解及免费在线批量转换工具